White Rabbit
Support Hub
Application Notes
Pico Second Timing for HEP (High Energy Physics)
In this note, we present the timing system architecture currently under development by Safran for the distribution of synchronized triggers.
Software-defined Timing: Embedded Timing for Next-generation Communication Systems
Explore HATI (High Accuracy Timing IP) core, utilizing FPGA resources alone, implementing IEEE-1588-2019 protocol for sub-nanosecond timing over Ethernet.
White Rabbit PTP License Activation
A specific license must be purchased in order to get full access to the IEEE 1588-2008 (PTPv2) module. When no license is provided, the PTP instance will start with the default profile and parameters. The user will only be allowed to configure the role of the port (Master, Slave or Disabled). The following table outlines…
FAQ
-
Can a WR device keep working with a single operating power supply module?
The short answer to this question is yes, a WR device can keep working with only one power supply.
The reason why these devices typically have two power supplies is due to redundancy purposes. Hence, the device is designed to keep working with only one of them in case the other fails.
When a PSU (Power Supply Unit) fails, a blinking red light can be seen. When this situation happens, it is necessary to remove carefully the affected power supply until the red light stops blinking. Then, press the start button on the device. This action should not be affected by any booting issue related to hardware changes due to the PSU.
It is highly relevant to restore the damaged power supply as soon as possible, because with a single PSU, the device depends completely on it and, in case it fails, the service will be stopped.
-
Why is a PTP license needed in a WRZ device and how can I upload it?
A specific license must be purchased in order to get full access to the IEEE 1588-2008 (PTPv2) module. We’ve created the document below to describe the technical differences and walk you through the process:
PTP License Technical Note -
How is the leap second file updated in WR devices?
Leap seconds are reviewed every 6 months.
Through the web page:
1. Go to “Timing/Misc/Configuration”. Then drag and drop the file into the box, or press “Browse” and select the file.
2. Press “Save”.
3. Reboot the device.
Through CLI:
1. Remove the file /media/data/usr/local/etc/leap-seconds.list if it exists:
rm /media/data/usr/local/etc/leap-seconds.list2. If the device has internet access, run the following command:
wget -O /media/data/usr/local/etc/custom-leap-seconds.list https://www.ietf.org/timezones/data/leap-seconds.list3. Otherwise, transfer the file from the local computer to the device through SCP in the same folder.
-
How can I retrieve the logdump file from a WR-Z device?
The log files can be retrieved through different procedures.
Using SSH:
Firstly, you need to introduce the following command on your PC:
ssh user@IP “source /etc/profile; wrz_logdump -o /tmp/”
Wait 30 seconds.
Finally, introduce the next command:
scp user@IP:/tmp/wrz-*.logdump
Note that user and IP are the typical WR-Z device credentials.
Otherwise, if what you want is the logdump file generated after reboot, the steps are almost the same. However, the file is stored within the following directory:
/root/.log/reboot
In case you want to check if this file is the one generated in your last reboot, you should introduce the next commands:
cat /root/.log/reboot/.last_reboot
ll /root/.log/reboot/*.logdump
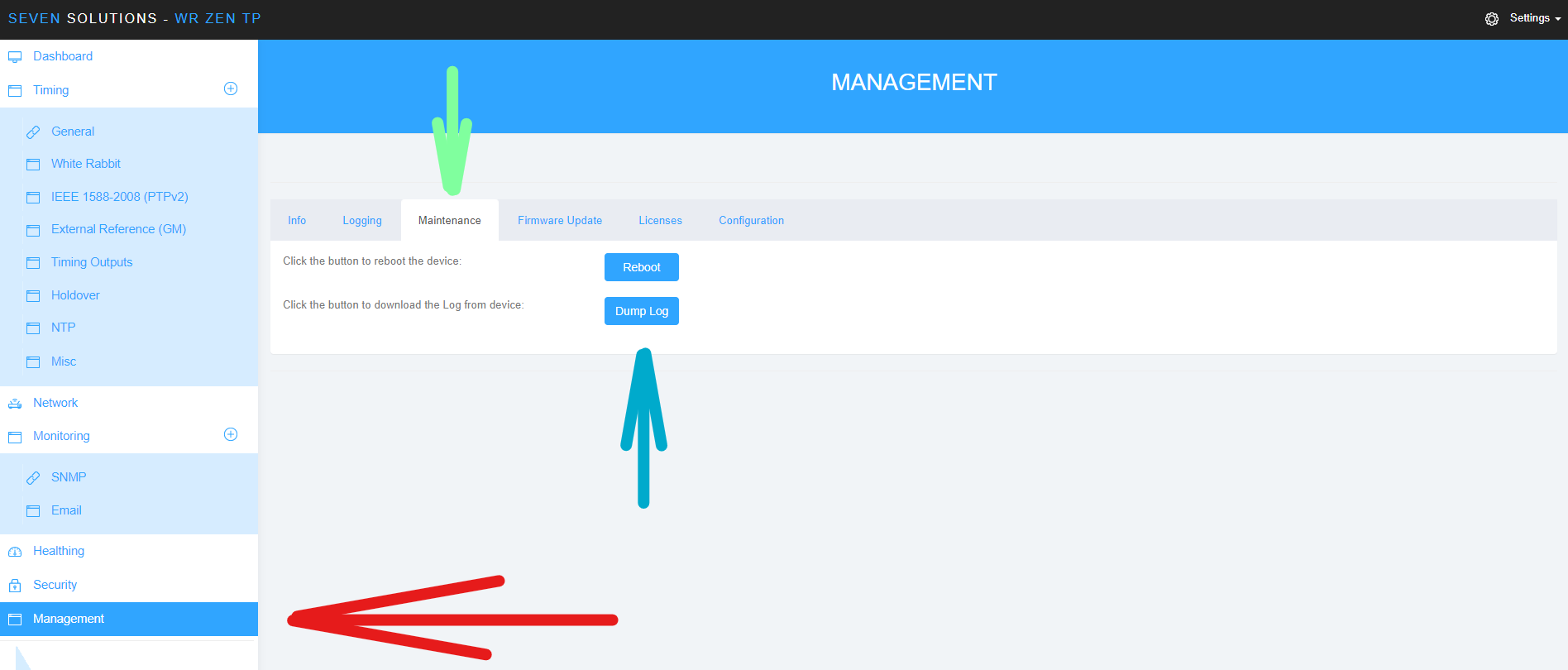
Using the web page:
Management -> Maintenance -> Dump Log
-
Can I use NTP as an active reference to discipline the internal oscillator of a WR device?
No. Due to its poor performance, NTP is always in survey mode, and, thus, it cannot actively discipline the local clock.
Log Support Ticket