Create a Basic GNSS Simulation Scenario
Tutorial
LINK FOR THIS SCENARIO | GITHUB
GSG-8 is the newest positioning, navigation, and timing test solution offered through Orolia’s GSG family of simulators, and powered by Skydel Simulation Engine. It was developed to deliver the highest standard of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) signal testing and sensor simulation performance in an easy to use, upgradable and scalable platform.
This document explains how to start a first basic simulation with a GSG-8.
1.1. Start SKYDEL and Create a New Configuration
The GSG-8 hardware model that can be used to run this simulation are:
| GSG-821 | GSG-831 | GSG-842/Broadsim |
|---|---|---|
| 2 RF Outputs | 3 RF outputs | 4 RF outputs |
| 1 GPU/2 SDR | 1GPU/3 SDR | 2 GPU/4 SDR |
To launch Skydel on a Linux system, simply type Skydel-sdx in the terminal.
In Windows, locate Orolia’s Skydel in the start menu and click on it.

Click “Continue”, and then Select “New Configuration”.
1.2. Add an output
To add an output, navigate to Settings – Output.

Select the DTA-2115B in the dropdown list and click the Add button twice.

1.3. Add signals
- Click on Edit in the Radio setting to set your radio configuration.

- Click on Signal selection Edit to select your signal.GPS: L1 C/A, L1C, L2C
- GLONASS: G1, G2
- Galileo: E1
- BeiDou: B1
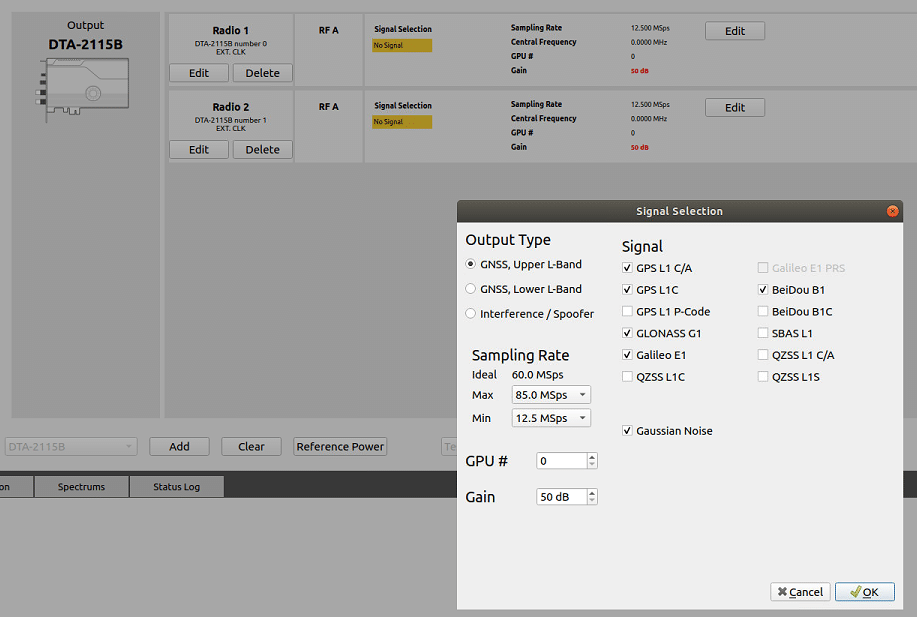
For this study case we will select GPSL1 CA in GNSS, Upper L-Band and GPS L2C in GNSS, Lower L-Band with the sampling rate of 50 MSps.
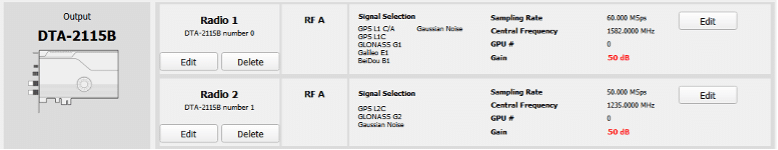
1.4. Set vehicle position
Next, we will configure our vehicle on a circular position.
Go to Settings –> Vehicle –> Body to set your vehicle position
For this case we use this position:
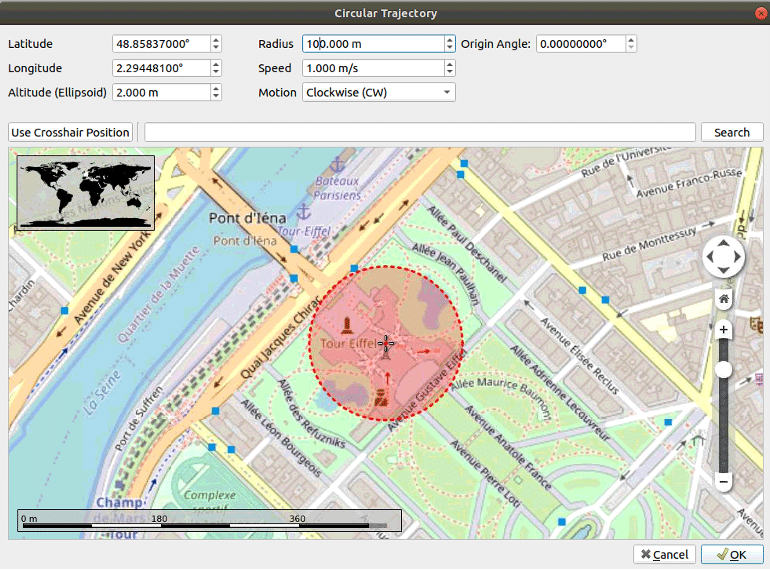
Click on Ok to save your configuration.
1.5. Connection to a receiver
We then connect a U-Blox receiver to the computer.
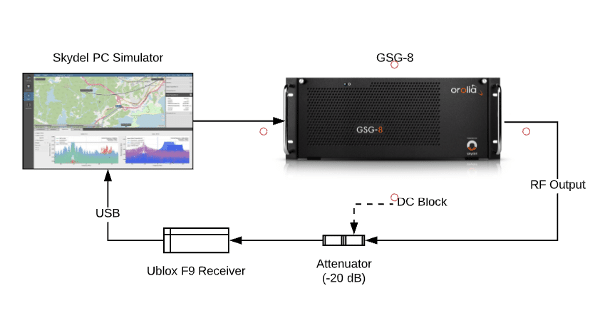
Go to menu Receiver and start by clicking the Connect button and choosing your receiver from the list of available ports.
1.6. Run the simulation
Click on start to run your simulation.

The simulator state will change to Initializing for approximately 2-3 seconds and if the hardware setup is properly done, the state will then change to Streaming RF. Now the simulation is running.

Then click on cold start on the receiver tab.

Go to the spectrums tab, and you see this view:


Check Show receiver on the constellation tab and go to the Map view:

Go to the Deviation tab:

You can also connect the receiver to a Windows computer and load the U-center application to observe the signals.

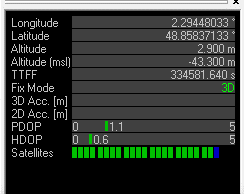
After a few minutes, we can see that the receiver is tracking the signals well and the position of the vehicle is clearly visible in the window.
1.7. Log files (raw data)
The logging settings allow the user to control how Skydel logs data during a simulation.
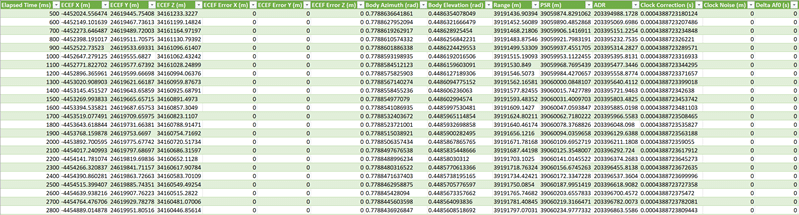
Check raw logging and Rinex Logging to log simulation data such as satellite trajectories, receiver trajectories, and signal power levels. You may also specify the desired update rate at which data are logged.

This is what the csv file you get looks like:
Conclusion:
The GSG-8 is a powerful GNSS simulator which allows the user to simulate simple simulations as presented in this document to the most complex including spoofers, jammers or HIL systems.
